This post outlines methods based on Large Language Models (LLMs), ordered from simpler to more complex approaches. While complex methods often yield better results, they require more effort to implement.
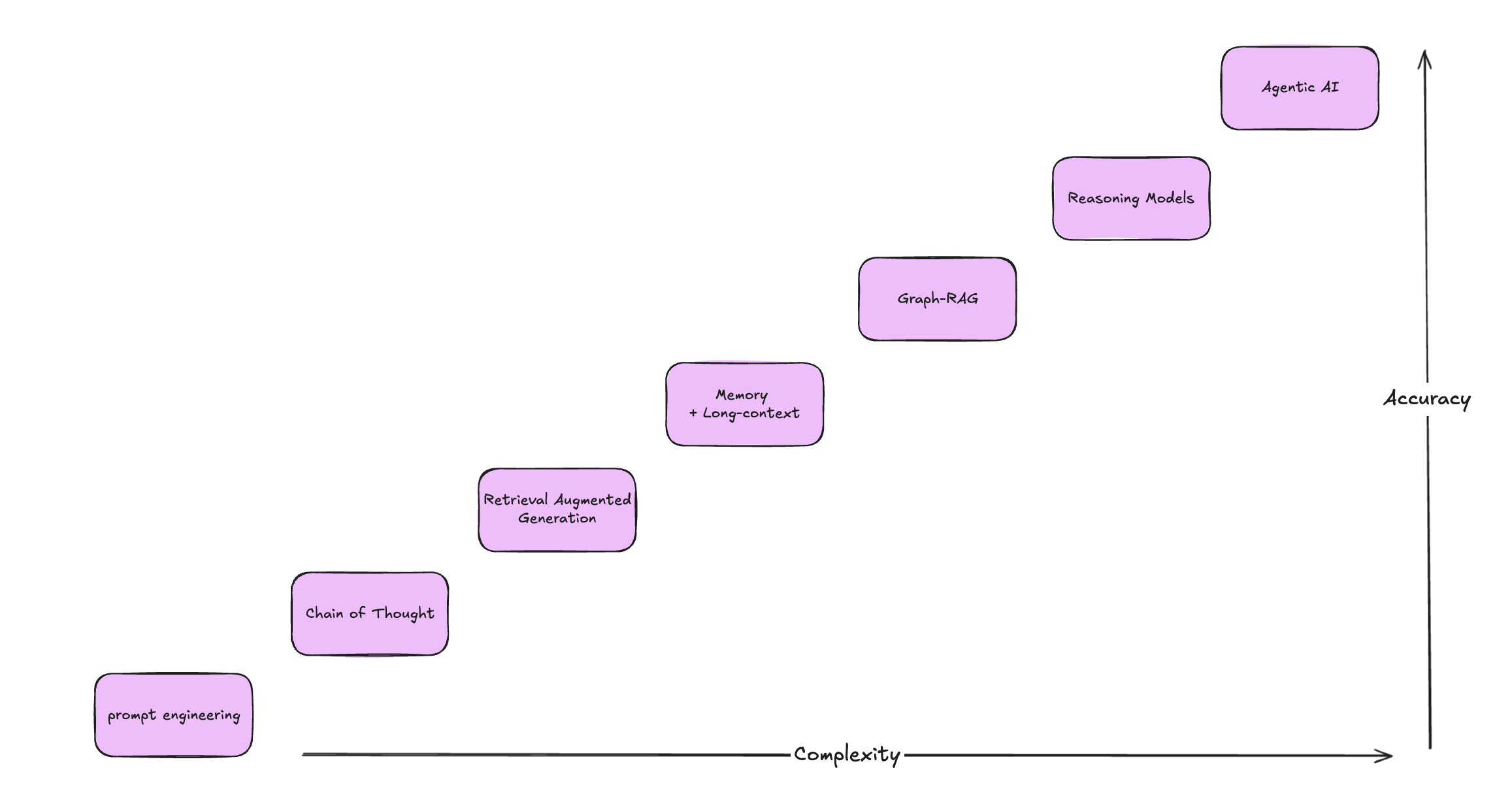
1 Prompt Engineering
2 Chain of Thought
3 Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
4 Memory-Based Systems ve Long-Context LLMs
5 Graph RAG
6 Reasoning Models
7 Agents
1. Prompt Engineering
You should try it out in the first phases of the project. Even though people do not care much about prompts, better-written and structured prompts would solve your problem without needing a more complex approach. I'll share more about prompt engineering soon.
2. Chain of Thought
It is actually more like an advanced prompt engineering technique. We're giving out examples and saying the model to explain step by step. You should definitely test it out with different styles of prompts for this and other prompt engineering techniques. There's also another concept called Few-shot prompting, which is giving different query-response pairs to the models.
E.g from ARC benchmark:
{ "id": "Mercury_7220990", "question": "Which factor will most likely cause a person to develop a fever?", "choices": { "text": [ "a leg muscle relaxing after exercise", "a bacterial population in the bloodstream", "several viral particles on the skin", "carbohydrates being digested in the stomach", ], "label": ["A", "B", "C", "D"], }, "answerKey": "B", }, { "id": "MCAS_2007_8_5189", "question": "Lichens are symbiotic organisms made of green algae and fungi. What do the green algae supply to the fungi in this symbiotic relationship?", "choices": { "text": ["carbon dioxide", "food", "protection", "water"], "label": ["A", "B", "C", "D"], }, "answerKey": "B", },
3. Retrieval Augmented Generation
RAG has changed how we interact with Language Models in our lives. There are prob thousands of Chat with ..(docs, pdf, github repo, etc.) applications. It's basically giving the right context to the LLM, so it can answer all of your questions based on the data it's fed. I already gave a talk at the company and built multiple rag projects.
So, I'll probably create another post to talk more about it. But, just know this, the retrieval engine should work perfectly to prevent hallucinations. Otherwise all the answers will be based on different context.
4. Memory-Based Systems ve Long-Context LLMs
We can say it's totally different from RAG, but at the same time, limited. You can feed all your data to an LLM that supports larger context windows. You can give books, documents, or anything if LLM supports that modality. Unfortunately, there aren't many models that support large context windows.
There's a technique called RoPE for larger context windows. One of the examples for this is ChatGPT. If you ask a question about a different thread, chatgpt can answer that. How?
Simple! There's a memory list, and whenever you finish a thread, ChatGPT summarizes each thread or topic discussed in the thread, + adds that summary to the memory list. And when you ask something about the past, ChatGPT goes to this memory to memorize.
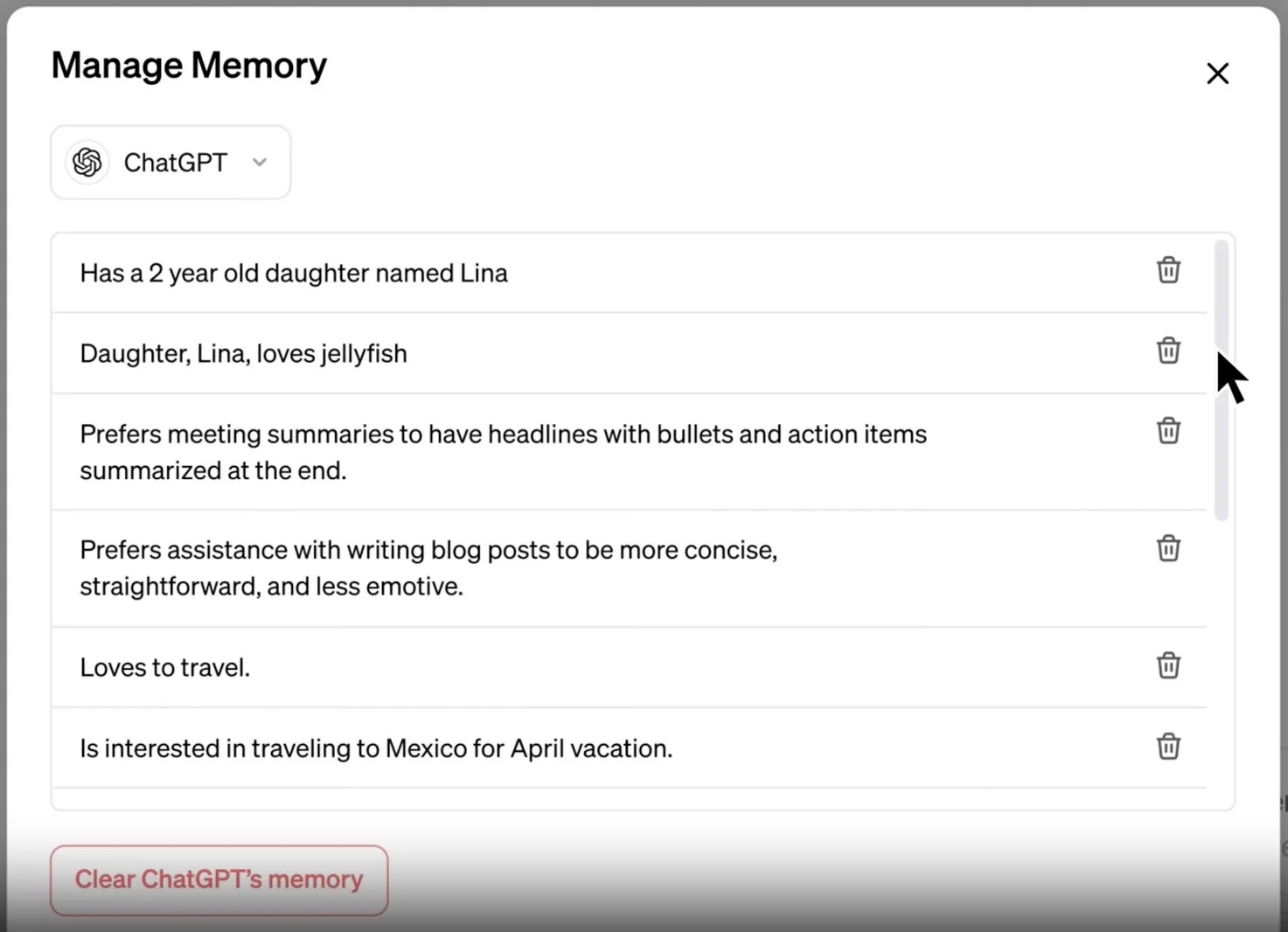
chatgpt memory
5. Graph RAG
While the standard RAG works based on the embeddings and documents, Graph RAG works based on a network-like kind of structure. When you ask sth. First, it finds the most related nodes and interconnections to generate an answer. Personally, I don't believe that many use cases need Graph RAG. And it's really hard to implement. (esp. data cleaning part)
6. Reasoning Models
After explaining all those other techniques, don't forget that an LLM only tries to predict the next token. That's why sometimes they're not working perfectly. Especially in the topics that need more reasoning, they give wrong answers + say Sorry, here's the right answer.'
Reasoning models are trained with <think></think> tags and longer thinking prompts. Results in spending more GPUs to think and reason! It simulates human thinking in a computer way. :)
7. Agents
Of course, it's questionable to think that Agentic AI is always works best! Wrong, there are still a lot of security issues in MCP!
If you're really interested, read this blog from Palo Alto Networks. MCP Security Exposed: What You Need to Know Now
But it delivers impressive results. By combining different tools and planning steps, they can automate tasks easily. Agents can decide which tools to use and reflect on their decisions before taking action.
For example, turning RAG into a tool and integrating it with an agent creates what's called "Agentic RAG." While full autonomy is still challenging, in the next 1–3 years, some job roles could realistically be handled by agents. We may also see agent teams that communicate, act like employees, or even manage other agents.
I love this architecture image from Langgraph.
Check out this MCP Security framework by Google.